We are one of the leading companies in research, development and manufacturing of pharmaceutical products for third parties
We offer Liquid-filled Capsules (Liquidcap) and Microgranules technologies
LIQUIDCAP
Liquidcap technology makes it possible to manufacture hard capsules filled with liquid or semi-solid contents.
These capsules are designed to optimize the bioavailability of active ingredients, in order to obtain therapeutical advantages as compared to other traditional dosage forms.

APPLICATIONS
| API characteristics | Target | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Low solubility (classes II and IV) | Increase of solubility / absorption | Enzalutamide, Olaparib, Nintedanib |
| Slow absorption | Increase of absorption speed | Etoricoxib, Tadalafil, Ibuprofen |
| Instability | Increase of stability | Cholecalciferol, Tretinoin |
| High potency / Low dosage | Dosage homogeneity | Lubiprostone, Calcitriol |
| Liquid or with low melting point | Simple solid formulation | Simethicone, Liquid and semi-solid vegetable extracts |
COMPARISON WITH SOFT-GEL CAPSULES
Faster speed of action
The walls of the hard capsule are thinner than those of a soft-gel capsule. Therefore, the hard capsules disintegrate and release their contents at a faster pace.Higher stability of the active component
Rigid capsules are less permeable to humidity and oxygen than soft-gel capsules. Therefore, it is possible to guarantee excellent stability of the active components, particularly those sensitive to humidity and oxidation.Higher stability of the dissolution profile
Some active ingredients and excipients induce polymerization of the gelatin, preventing it to dissolve in water. This process is known as gelatin crosslinking. One of the key advantages of the Liquidcap technology is that the capsules can be made of a variety of alternative materials, such as hypromellose or pullulan, thus making it possible to avoid the crosslinking and maintaining the dissolution kinetics throughout the shelf life of the product.Simple and cost-effective manufacturing process
The manufacturing process encompasses three stages: preparation of the component solution/suspension, filling of capsules and sealing of capsules.MICROGRANULES
Microgranules technology consists in applying different functional coatings to small spherical particles containing the active ingredient.
The microgranules form a multi-particulate system that allows to adjust in a very precise manner the dissolution profile of the formulations containing one or several active ingredients.
1. Modified Release
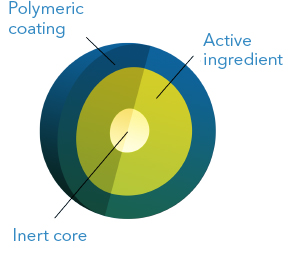
This technology consists in applying one or more layers of coating to spherical cores
containing the active ingredient. Depending on the desired dissolution profile, the coating
is done using soluble, insoluble or pH-dependent solubility polymers. Therefore, it is
possible to obtain extended, delayed, or colonic release profiles. It is also possible to
obtain pulsatile release and to combine two or more microgranule populations with different
dissolution profiles into one dosage form.
Microgranules can be filled into capsules, formulated as suspension, or compressed into
tablets, without losing their properties. For better mouthfeel, it is possible to reduce
the diameter of microgranules to less than 500 microns (micropellets).
One of the key advantages of microgranules is that they allow to combine in one
pharmaceutical form different active components, each with its required dissolution
profile.
pH-independent Extended Release
Tonibral XR
(memantine HCI)
Gador
pH-dependent Extended Release
Dilantrend AP
(carvedilol phosphate)
Argentia

Pulsatile Release
Dexopral (dexlansoprazol)
Roemmers
Delayed Release
Esogastrosedol
(esomeprazole
magnesium)
Argentia
2. Increased Solubility
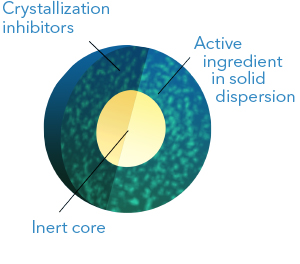
This technology enables the development of increased solubility formulations in which the
active ingredient is in amorphous (non-crystalline) state and forming a solid dispersion.
The solid dispersion is obtained by dissolving the active component together with an
hydrophilic polymer in a suitable solvent and then spraying this solution onto inert cores.
The technology allows the addition of crystallization inhibitors, surfactants and
disintegrating agents to enhance the formulation performance.

Solid dispersion without surfactants
Panastat 200
(itraconazol)
Panalab

Solid dispersion with surfactants
Reduprost Duo
(dutasteride)
Raffo
3. Increased stability
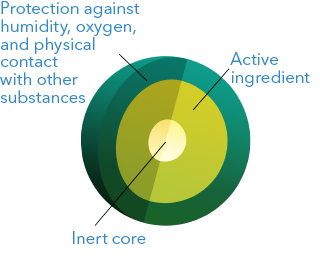
This technology makes it possible to enhance the stability of the active ingredients through the application of a soluble polymeric coating in cases such as:
- Combination of incompatible active ingredients: by avoiding the physical contact among incompatible ingredients, the stability is enhanced, for example: Tenofovir coated granules can be compressed with incompatible antivirals in the same tablet in a stable way.
- Active ingredients sensitive to humidity: it is possible to apply a coating with a high-barrier polymer against humidity. For example, the peptide Linaclotide is stabilized in microgranules by applying a PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) coating membrane.
- Volatile active ingredients: Dimethyl fumarate is formulated in coated microgranules to prevent the volatilization of the active ingredient, thus achieving stability for prolonged periods.
4. Taste masked
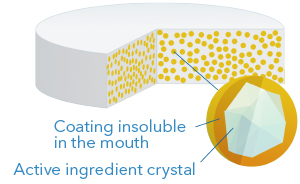
This technology consists in applying a membrane directly over the crystals of active ingredients, thus obtaining taste masked particles of very small diameter (200-600 microns), which is ideal for suspensions as well as for dispersible or chewable tablets. The coating is designed to be insoluble in the mouth but to be rapidly soluble in the stomach, so as not to interfere with the bioavailability of the active ingredient.
Microcapsules for suspension
Macromax 2G
(azithromycin)
Investi Farma
Compressible microcapsules
Chewable Febratic Tablets
(Ibuprofen)
Roemmers
Contact
Pharm. Gerardo Wessolovski
gerardo.wessolovski@novocap.comGabriela Vazquez, Customer Services
gabriela.vazquez@novocap.com